Method 319 Compliant System
Title 40 of the Code of Federal Regulations Part 63, Subpart GG (“40 CFR Part 63”), also known as the National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (“NESHAP”) established (i) standards; (ii) test methods and procedures; (iii) monitoring requirements; (iv) record keeping requirements and (v) reporting requirements for aerospace manufacturing and rework facilities.
Specifically with respect to paint application and removal,
the EPA requires:
- All operations to be conducted in a spray booth or hangar;
- Air flow must be downward or across the part and must be exhausted through a control device; and
- A control device can be a dry particulate filter (also known as a paint arrestor) or water wash system but must meet certain minimum standards.
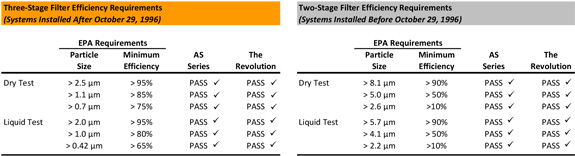
The EPA developed a test protocol known as Method 319 to determine if a dry particulate filter/paint arrestor complies with 40 CFR Part 63. Method 319 attempts to simulate dry and wet overspray characteristics of hazardous air pollutants (“HAP”) and volatile organic compounds (“VOC”).
Viskon-Aire NESHAP Resources
Viskon-Aire’s NESHAP 319 Compliant System
EPA Method 319 Test Report (AS Series)
EPA Method 319 Test Report (Revolution)
Polyester Overspray Media (Literature)
Additional Resources

EPA Rule and Implementation Information for the Aerospace Industry

